Difference between revisions of "BrainRegionFMM NC PH MEC"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
* [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.large.jpg Contributions of Diencephalon to Recognition Memory] - see [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.expansion.html Reference] | * [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.large.jpg Contributions of Diencephalon to Recognition Memory] - see [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.expansion.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.large.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.large.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/images/nrn1299-f2.jpg Mammillary bodies: two memory systems in one] - see [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/fig_tab/nrn1299_F2.html Reference] | * [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/images/nrn1299-f2.jpg Mammillary bodies: two memory systems in one] - see [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/fig_tab/nrn1299_F2.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/images/nrn1299-f2.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/images/nrn1299-f2.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.scholarpedia.org/w/images/6/63/Taube_Figure_5a.png Head Direction Cell Circuit] - see [http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Head_direction_cells Reference] | * [http://www.scholarpedia.org/w/images/6/63/Taube_Figure_5a.png Head Direction Cell Circuit] - see [http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Head_direction_cells Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.scholarpedia.org/w/images/6/63/Taube_Figure_5a.png" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.scholarpedia.org/w/images/6/63/Taube_Figure_5a.png" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v3/n2/images/nrn726-f3.jpg McNaughton Spatial Processing Network] - see [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v3/n2/fig_tab/nrn726_F3.html Reference] | * [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v3/n2/images/nrn726-f3.jpg McNaughton Spatial Processing Network] - see [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v3/n2/fig_tab/nrn726_F3.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v3/n2/images/nrn726-f3.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v3/n2/images/nrn726-f3.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.scholarpedia.org/w/images/thumb/f/f2/ITCortex_pathway.jpg/400px-ITCortex_pathway.jpg Visual Path to Hippocampus] - see [http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Inferior_temporal_cortex Reference] | * [http://www.scholarpedia.org/w/images/thumb/f/f2/ITCortex_pathway.jpg/400px-ITCortex_pathway.jpg Visual Path to Hippocampus] - see [http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Inferior_temporal_cortex Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.scholarpedia.org/w/images/thumb/f/f2/ITCortex_pathway.jpg/400px-ITCortex_pathway.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.scholarpedia.org/w/images/thumb/f/f2/ITCortex_pathway.jpg/400px-ITCortex_pathway.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png Amygdala and its network] - see [http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin Reference] | * [http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png Amygdala and its network] - see [http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
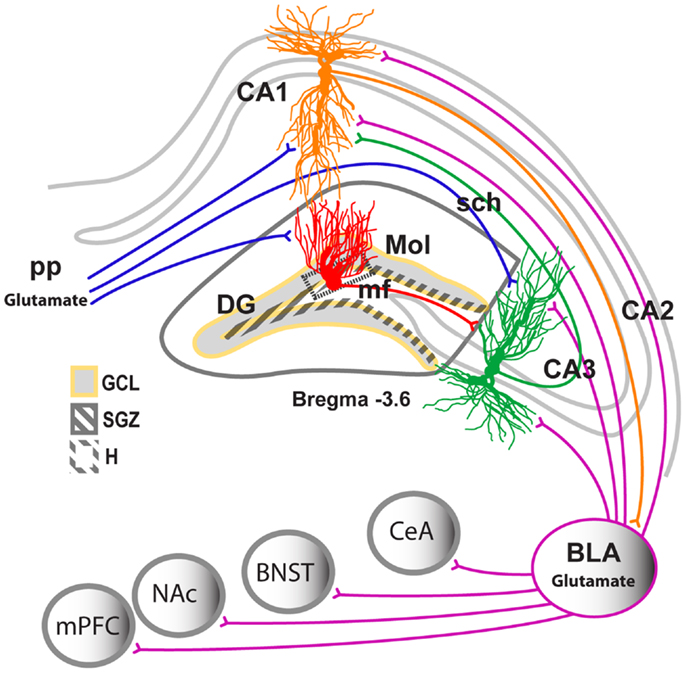
* [http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/46459/fpsyt-04-00061-HTML/image_m/fpsyt-04-00061-g002.jpg Neuronal projections in the hippocampus] - see [http://journal.frontiersin.org/Journal/10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00061/full Reference] | * [http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/46459/fpsyt-04-00061-HTML/image_m/fpsyt-04-00061-g002.jpg Neuronal projections in the hippocampus] - see [http://journal.frontiersin.org/Journal/10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00061/full Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/46459/fpsyt-04-00061-HTML/image_m/fpsyt-04-00061-g002.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/46459/fpsyt-04-00061-HTML/image_m/fpsyt-04-00061-g002.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
Revision as of 09:06, 7 September 2015
Medial Entorhinal Cortex
@@Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> BrainAreaFMM -> BrainRegionFMM_NC_PH_MEC
This page covers biological details of component Medial Entorhinal Cortex. Region is part of aHuman target integrated biological model.
- Top-down path to region: Cerebral Cortex -> Parahippocampal Lobe (NC.LOBE.PH) -> Anterior Parahippocampal Gyrus (FMM.NC.PHA) -> Rhinal Cortex (NC.PHA.RH) -> Entorhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.ET) -> Medial Entorhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.MEC) (see Mind Maps)
- Type: cortex
- Brain area: Forebrain - Memory Management Area
- Brodmann ID: 28
- Role: processor
- Function: Memory consolidation, basic, view independent position
- Notes to function: spatial input to HC; grid cells; path integration computations based on a global frame of reference, primarily using internally generated, self-motion cues and external input about environmental boundaries and scenes; provides hippocampus with coordinate system that underlies spatial context of experience
(generated)
Components
(generated)
- no child items defined
Connectivity
(generated)
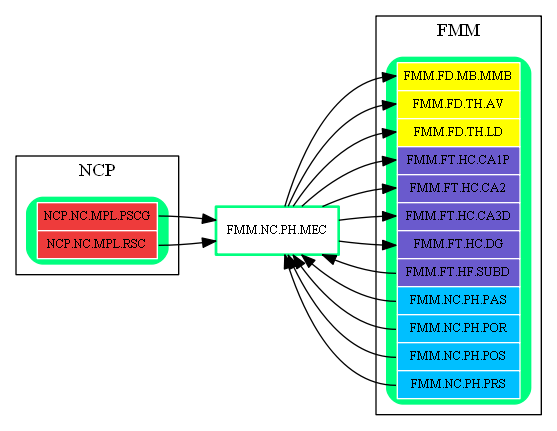
Inbound Region Connections:
| Source Area | Source Region | Source Name | Type | Reference |
| FMM | FMM.FT.HF.SUBD | Distal Subiculum | excitatory-glu | Attractor Network in Hippocampus (SUB -> EC, abstract) |
| FMM.NC.PH.PAS | Parasubiculum | feedforward-glu | (unknown reference) | |
| FMM.NC.PH.POR | Postrhinal Cortex | feedforward-glu | Entorhinal Cortex Inputs and Outputs (TFTH -> EC, abstract) | |
| FMM.NC.PH.POS | Postsubiculum | feedforward-glu | Head Direction Cell Circuit (PSUB -> EC, abstract) | |
| FMM.NC.PH.PRS | Presubiculum | feedforward-glu | Attractor Network in Hippocampus (PRESUB -> EC, abstract) | |
| NCP | NCP.NC.MPL.PSCG | Posterior Cingulate Cortex | feedforward-glu | McNaughton Spatial Processing Network (PCGRSP -> EnthCortex, abstract) |
| NCP.NC.MPL.RSC | Retrosplenial Cortex | feedforward-glu | McNaughton Spatial Processing Network (PCGRSP -> EnthCortex, abstract) |
Outbound Region Connections:
| Target Area | Target Region | Target Name | Type | Reference |
| FMM | FMM.FD.MB.MMB | Medial Mammillary Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Mammillary bodies: two memory systems in one (MedialEC -> MMB, abstract) |
| FMM.FD.TH.AV | Anteroventral Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Contributions of Diencephalon to Recognition Memory (EC -> AN, abstract) | |
| FMM.FD.TH.LD | Lateral Dorsal Nucleus of Thalamus | excitatory-glu | Contributions of Diencephalon to Recognition Memory (EC -> LD, abstract) | |
| FMM.FT.HC.CA1P | Proximal CA1 of Hippocampus | excitatory-glu | Neuronal projections in the hippocampus (ET -> CA1, abstract) | |
| FMM.FT.HC.CA2 | Dorsolateral Cornu Ammonis of Hippocampus | excitatory-glu | Amygdala and its network (EC -> HC, abstract) | |
| FMM.FT.HC.CA3D | Distal CA3 of Hippocampus | excitatory-glu | Neuronal projections in the hippocampus (ET -> CA3, abstract) | |
| FMM.FT.HC.DG | Dentate Gyrus | excitatory-glu | Neuronal projections in the hippocampus (ET -> DG, abstract) |
Thirdparty Circuits
(generated)






References
(generated)
- http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.expansion.html
- http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/fig_tab/nrn1299_F2.html
- http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Head_direction_cells
- http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v3/n2/fig_tab/nrn726_F3.html
- http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Inferior_temporal_cortex
- http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin
- http://journal.frontiersin.org/Journal/10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00061/full