Difference between revisions of "BrainCenterNC PHA RH"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
| [[BrainCenterFAM_FT_AM|Amygdala]] (FAM.FT.AM) || [http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/dl/free/0071402357/156721/figure350_1.html Principal Connections of Hippocampus (AM -> EC, abstract)] | | [[BrainCenterFAM_FT_AM|Amygdala]] (FAM.FT.AM) || [http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/dl/free/0071402357/156721/figure350_1.html Principal Connections of Hippocampus (AM -> EC, abstract)] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[ | + | | [[BrainCenterFD_TH_CR|Cognitive Thalamus]] (FD.TH.CR) || [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.expansion.html Contributions of Diencephalon to Recognition Memory (MID -> EC, abstract)] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[BrainCenterFMM_FT_HF|Hippocampal Formation]] (FMM.FT.HF) || [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/14/11/714/F1.expansion Attractor Network in Hippocampus (SUB -> EC, abstract)] | | [[BrainCenterFMM_FT_HF|Hippocampal Formation]] (FMM.FT.HF) || [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/14/11/714/F1.expansion Attractor Network in Hippocampus (SUB -> EC, abstract)] | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
| [[BrainCenterFD_HT|Hypothalamus]] (FD.HT) || [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/fig_tab/nrn1299_F2.html Mammillary bodies: two memory systems in one (MedialEC -> MMB, abstract)] | | [[BrainCenterFD_HT|Hypothalamus]] (FD.HT) || [http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/fig_tab/nrn1299_F2.html Mammillary bodies: two memory systems in one (MedialEC -> MMB, abstract)] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[ | + | | [[BrainCenterFD_TH_CR|Cognitive Thalamus]] (FD.TH.CR) || [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.expansion.html Contributions of Diencephalon to Recognition Memory (EC -> MDmc, abstract)] |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[BrainCenterFD_TH_MR|Motor Thalamus]] (FD.TH.MR) || [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.expansion.html Contributions of Diencephalon to Recognition Memory (EC -> LD, abstract)] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[BrainCenterFD_TH_SR|Sensory Thalamus]] (FD.TH.SR) || [http://learnmem.cshlp.org/content/18/6/384/F1.expansion.html Contributions of Diencephalon to Recognition Memory (Perirhinal -> mPULV)] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[BrainCenterFEC_FT_BG|Basal Ganglia]] (FEC.FT.BG) || [http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/nucleus-accumbens.jpg Nucleus Accumbens (EC -> NACC, abstract)] | | [[BrainCenterFEC_FT_BG|Basal Ganglia]] (FEC.FT.BG) || [http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/nucleus-accumbens.jpg Nucleus Accumbens (EC -> NACC, abstract)] | ||
Revision as of 09:50, 31 July 2015
Rhinal Cortex
@@Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> BrainCenterNC_PHA_RH
This page covers biological details of component group Rhinal Cortex. Component group is part of aHuman target integrated biological model.
- Top-down path to center: Cerebral Cortex -> Parahippocampal Lobe (NC.LOBE.PH) -> Anterior Parahippocampal Gyrus (FMM.NC.PHA) -> Rhinal Cortex (NC.PHA.RH) (see Mind Maps)
- Function: Memory consolidation and olfaction perception
(generated)
Components
(generated)
Component items:
- Entorhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.ET): Memory consolidation
- Lateral Entorhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.LEC): Memory consolidation, emotional aspects
- Medial Entorhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.MEC): Memory consolidation, basic, view independent position
- Perirhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.PER): Associate different visual views of objects and their various nonvisual attributes
- Piriform Cortex (NSA.NC.PH.PIR): Perception of smells, primary olfactory cortex
- Prepyriform Cortex (NSA.NC.PH.PRP): Perception of smells, relay via MD to PFC
Connectivity
(generated)
Internal Regions Connections:
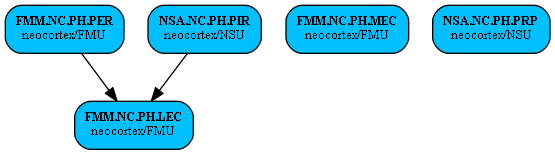
| Source Region | Target Region | Reference |
| Perirhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.PER) | Lateral Entorhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.LEC) | Visual Path to Hippocampus (PRPH -> ER, abstract) |
| Piriform Cortex (NSA.NC.PH.PIR) | Lateral Entorhinal Cortex (FMM.NC.PH.LEC) | KIV model of cortico-hippocampal formation with subcortical projections for motor actions (PC -> EC, abstract) |
External Connections:
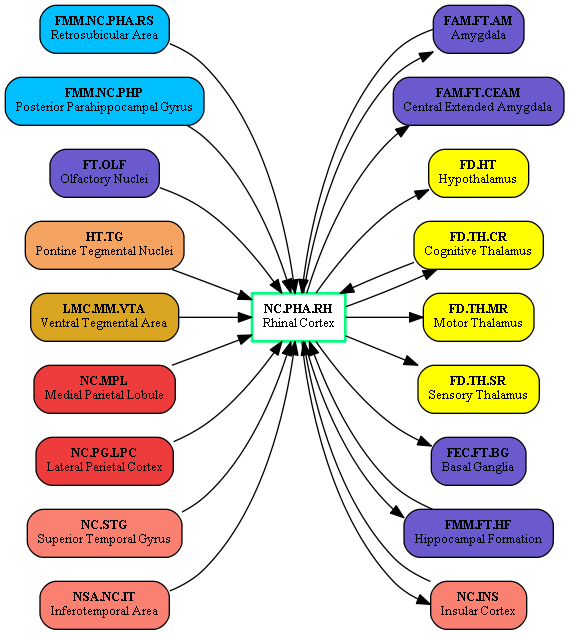
External Inbound Center Connections:
External Outbound Center Connections: