Difference between revisions of "BrainRegionLAC FD HT MPO"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
| || [[BrainRegionLAC_HL_TGS_PE5|LAC.HL.TGS.PE5]] || Peritrigeminal Nucleus || excitatory-glu || (unknown reference) | | || [[BrainRegionLAC_HL_TGS_PE5|LAC.HL.TGS.PE5]] || Peritrigeminal Nucleus || excitatory-glu || (unknown reference) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[ | + | | [[BrainAreaNDM|NDM]] || [[BrainRegionNDM_FD_TH_PV|NDM.FD.TH.PV]] || Paraventricular Nucleus of Thalamus || excitatory-glu || (unknown reference) |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 01:47, 24 January 2016
Median Preoptic Nucleus
@@Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> BrainAreaLAC -> BrainRegionLAC_FD_HT_MPO
This page covers biological details of component Median Preoptic Nucleus. Region is part of aHuman target integrated biological model.
- Top-down path to region: Forebrain Diencephalon -> Hypothalamus (FD.HT) -> Anterior Hypothalamus Area (LAC.FD.HT.AHT) -> Chiasmatic Area (LAC.FD.HT.CHS) -> Preoptic Nucleus (LAC.FD.HT.PO) -> Median Preoptic Nucleus (LAC.FD.HT.MPO) (see Mind Maps)
- Type: nucleus
- Brain area: Lower Brain - Autonomous Control Area
- Role: processor.autonomic
- Function: generates thirst
- Notes to function: Drinking decreases noradrenaline release in median preoptic nucleus
(generated)
Components
(generated)
- no child items defined
Connectivity
(generated)
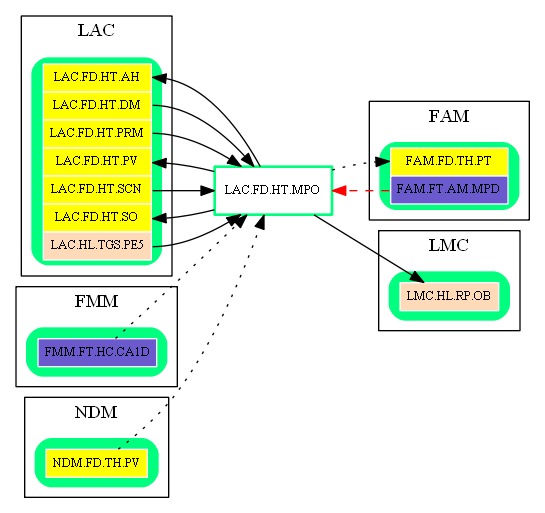
Inbound Region Connections:
| Source Area | Source Region | Source Name | Type | Reference |
| FAM | FAM.FT.AM.MPD | Medial Posterior Dorsal Amygdaloid Nucleus | inhibitory-gaba | Role for serotonin in moral behavior (AMY -> HYP, abstract) |
| FMM | FMM.FT.HC.CA1D | Distal CA1 of Hippocampus | excitatory-glu | Feeling (HC -> HT, abstract) |
| LAC | LAC.FD.HT.DM | Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Eating and sleeping to survive (DMH -> MPO) |
| LAC.FD.HT.PRM | Premammillary Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) | |
| LAC.FD.HT.SCN | Suprachiasmatic Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance (SCH -> MPOA) | |
| LAC.HL.TGS.PE5 | Peritrigeminal Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) | |
| NDM | NDM.FD.TH.PV | Paraventricular Nucleus of Thalamus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
Outbound Region Connections:
| Target Area | Target Region | Target Name | Type | Reference |
| FAM | FAM.FD.TH.PT | Paratenial Nucleus of Thalamus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
| LAC | LAC.FD.HT.AH | Anterior Hypothalamic Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance (MPOA -> AH) |
| LAC.FD.HT.PV | Paraventricular Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance (MPOA -> PA) | |
| LAC.FD.HT.SO | Supraoptic Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance (MPOA -> SON) | |
| LMC | LMC.HL.RP.OB | Raphe Obscurus Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
Thirdparty Circuits
(generated)
- Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance - see Reference



References
(generated)
- http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf
- http://www.dana.org/Publications/ReportDetails.aspx?id=44217
- http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders