Difference between revisions of "BrainRegionLMC MM VTA"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[BrainAreaFAM|FAM]] || [[BrainRegionFAM_FT_BNST|FAM.FT.BNST]] || Bed Nucleus of Stria Terminalis || excitatory-glu || (unknown reference) | | [[BrainAreaFAM|FAM]] || [[BrainRegionFAM_FT_BNST|FAM.FT.BNST]] || Bed Nucleus of Stria Terminalis || excitatory-glu || (unknown reference) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || [[BrainRegionFAM_HP_PPN_RMTG|FAM.HP.PPN.RMTG]] || Rostromedial Tegmental Nucleus || inhibitory-gaba || [http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin Amygdala and its network (RMTG -> VTA)] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[BrainAreaFEC|FEC]] || [[BrainRegionFEC_FT_ACC_CORE|FEC.FT.ACC.CORE]] || Nucleus Accumbens Core || inhibitory-gaba || [http://neurowiki2012.wikispaces.com/Presynaptic+Mechanisms+of+Synaptic+Plasticity Reward circuit of human brain (NACC -> VTA, abstract)] | | [[BrainAreaFEC|FEC]] || [[BrainRegionFEC_FT_ACC_CORE|FEC.FT.ACC.CORE]] || Nucleus Accumbens Core || inhibitory-gaba || [http://neurowiki2012.wikispaces.com/Presynaptic+Mechanisms+of+Synaptic+Plasticity Reward circuit of human brain (NACC -> VTA, abstract)] | ||
| Line 66: | Line 68: | ||
| [[BrainAreaNDM|NDM]] || [[BrainRegionNDM_NC_AL_DACG|NDM.NC.AL.DACG]] || Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Area || modulatory-da || (unknown reference) | | [[BrainAreaNDM|NDM]] || [[BrainRegionNDM_NC_AL_DACG|NDM.NC.AL.DACG]] || Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Area || modulatory-da || (unknown reference) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | || [[BrainRegionNDM_NC_AL_FPC|NDM.NC.AL.FPC]] || Lateral Frontopolar Cortex || modulatory-da || [http:// | + | | || [[BrainRegionNDM_NC_AL_FPC|NDM.NC.AL.FPC]] || Lateral Frontopolar Cortex || modulatory-da || [http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin Amygdala and its network (VTA -> MPFC, abstract)] |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 108: | Line 110: | ||
<img src="http://www.impulsecontroldisorders.org/images/8-Urges9proof.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | <img src="http://www.impulsecontroldisorders.org/images/8-Urges9proof.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | ||
| − | * [http:// | + | * [http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png Amygdala and its network] - see [http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin Reference] |
| − | <img src="http:// | + | <img src="http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png" alt="unavailable"> |
Revision as of 09:22, 15 July 2015
Ventral Tegmental Area
@@Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> BrainAreaLMC -> BrainRegionLMC_MM_VTA
This page covers biological details of component Ventral Tegmental Area. Region is part of aHuman target integrated biological model.
- Top-down path to region: Midbrain Mesencephalon -> Ventral Tegmental Area (LMC.MM.VTA) (see Mind Maps)
- Type: nucleus
- Brain area: Lower Brain - Modulatory Contol Area
- Role: relay
- Function: Respond to novel stimuli, unexpected rewards, and reward predictive sensory cues
(generated)
Components
(generated)
Component items:
- Medial Ventral Tegmental Area
- Parabrachial Pigmented Area
- Paranigral Nucleus
- Parafasciculus Retroflexus Area
- Raphe Nucleus Linearis (LMC.HP.RP.LI): Release of 5-HT was only obtained on stimulation of this nucleus
- Rostral Linear Nucleus
Connectivity
(generated)
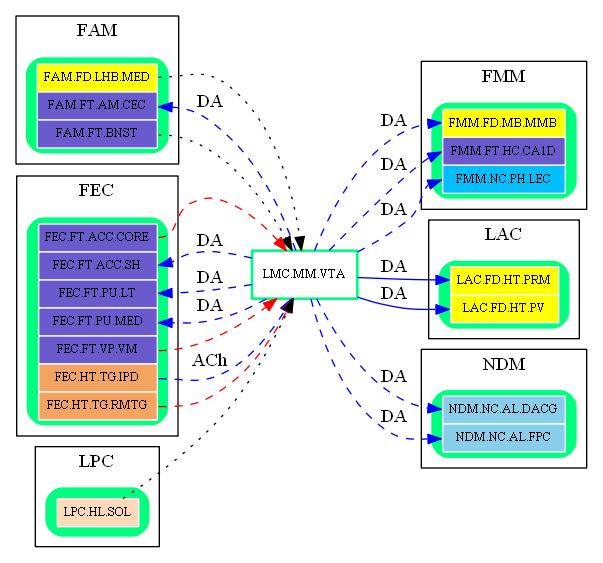
Inbound Region Connections:
| Source Area | Source Region | Source Name | Type | Reference |
| FAM | FAM.FT.BNST | Bed Nucleus of Stria Terminalis | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
| FAM.HP.PPN.RMTG | Rostromedial Tegmental Nucleus | inhibitory-gaba | Amygdala and its network (RMTG -> VTA) | |
| FEC | FEC.FT.ACC.CORE | Nucleus Accumbens Core | inhibitory-gaba | Reward circuit of human brain (NACC -> VTA, abstract) |
| LMC | LMC.HP.TG.VTG | Ventral Tegmental Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
Outbound Region Connections:
Thirdparty Circuits
(generated)



- Combining Novelty, Motivational Salience, and Reward to Control Attention and Learning - see Reference







References
(generated)
- http://brmlab.cz/project/brain_hacking/tdcs/pfc
- http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/fig_tab/nrn1299_F4.html
- http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v5/n1/fig_tab/nrn1299_F2.html
- http://www.impulsecontroldisorders.org/html/cravings.html
- http://www.springerimages.com/Images/LifeSciences/1-10.1007_s00359-004-0565-9-0
- http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders
- http://neurowiki2012.wikispaces.com/Presynaptic+Mechanisms+of+Synaptic+Plasticity
- http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Habenula
- http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin