Difference between revisions of "BrainRegionLAC FD HT PV"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
| || [[BrainRegionLAC_FD_HT_PO|LAC.FD.HT.PO]] || Preoptic Nucleus || excitatory-glu || [http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance (MPOA -> PA)] | | || [[BrainRegionLAC_FD_HT_PO|LAC.FD.HT.PO]] || Preoptic Nucleus || excitatory-glu || [http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance (MPOA -> PA)] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | || [[BrainRegionLAC_FD_HT_SCN|LAC.FD.HT.SCN]] || Suprachiasmatic Nucleus || excitatory-glu || ( | + | | || [[BrainRegionLAC_FD_HT_SCN|LAC.FD.HT.SCN]] || Suprachiasmatic Nucleus || excitatory-glu || [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html Food-entrainable circadian oscillator (SCN -> PVH)] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[BrainAreaLMC|LMC]] || [[BrainRegionLMC_MM_VTA|LMC.MM.VTA]] || Ventral Tegmental Area || modulatory-da || [http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders Physiology and pathophysiology of lower urinary tract (VTA -> PVN)] | | [[BrainAreaLMC|LMC]] || [[BrainRegionLMC_MM_VTA|LMC.MM.VTA]] || Ventral Tegmental Area || modulatory-da || [http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders Physiology and pathophysiology of lower urinary tract (VTA -> PVN)] | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
<img src="http://neuropolitics.org/connect-amygdala.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | <img src="http://neuropolitics.org/connect-amygdala.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg Food-entrainable circadian oscillator] - see [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html Reference] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <img src="http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg" alt="unavailable"height=300> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [http://www.dana.org/uploadedImages/Images/Content_Images/SenBodyFunc2_PR2007_cont.jpg Eating and sleeping to survive] - see [http://www.dana.org/Publications/ReportDetails.aspx?id=44217 Reference] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <img src="http://www.dana.org/uploadedImages/Images/Content_Images/SenBodyFunc2_PR2007_cont.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | ||
* [http://www.intechopen.com/source/html/40109/media/image1.jpeg Physiology and pathophysiology of lower urinary tract] - see [http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders Reference] | * [http://www.intechopen.com/source/html/40109/media/image1.jpeg Physiology and pathophysiology of lower urinary tract] - see [http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders Reference] | ||
| Line 99: | Line 107: | ||
* http://neuropolitics.org/defaultmay10.asp | * http://neuropolitics.org/defaultmay10.asp | ||
| + | * http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html | ||
| + | * http://www.dana.org/Publications/ReportDetails.aspx?id=44217 | ||
* http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders | * http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders | ||
* http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf | * http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf | ||
Revision as of 10:00, 2 September 2015
Paraventricular Nucleus
@@Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> BrainAreaLAC -> BrainRegionLAC_FD_HT_PV
This page covers biological details of component Paraventricular Nucleus. Region is part of aHuman target integrated biological model.
- Top-down path to region: Forebrain Diencephalon -> Hypothalamus (FD.HT) -> Anterior Hypothalamus Area (LAC.FD.HT.AHT) -> Tuberal Area (LAC.FD.HT.TUB) -> Paraventricular Nucleus (LAC.FD.HT.PV) (see Mind Maps)
- Type: nucleus
- Brain area: Lower Brain - Autonomous Control Area
- Role: relay
- Function: Regulate appetite and autonomic functions
(generated)
Components
(generated)
Component items:
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Magnocellular Division
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Magnocellular Division - Anterior Magnocellular Part
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Magnocellular Division - Medial Magnocellular Part
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Magnocellular Division - Posterior Magnocellular Part
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Magnocellular Division - Posterior Magnocellular Part Lateral Zone
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Magnocellular Division - Posterior Magnocellular Part Medial Zone
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Parvicellular Division
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Descending Division
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Descending Division - Dorsal Parvicellular Part
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Descending Division - Forniceal Part
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Descending Division - Lateral Parvicellular Part
- Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus Descending Division - Medial Parvicellular Part, Ventral Zone
Connectivity
(generated)
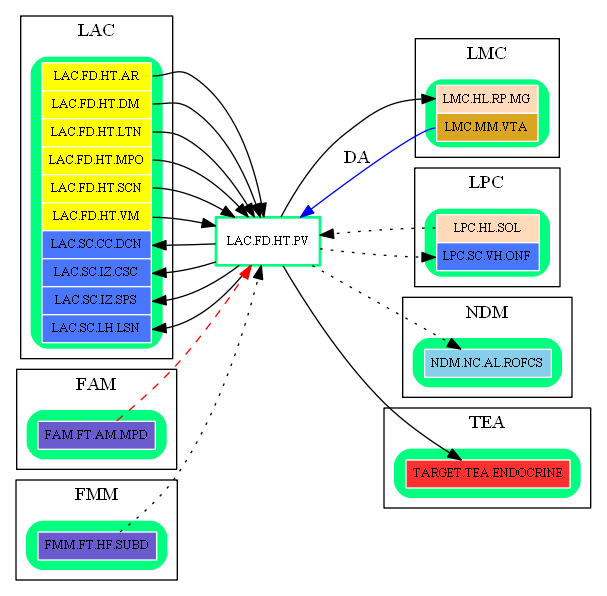
Inbound Region Connections:
Outbound Region Connections:
| Target Area | Target Region | Target Name | Type | Reference |
| LAC | LAC.FD.HT.VM | Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
| LAC.SC.CC.DCN | Dorsal Commissural Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) | |
| LAC.SC.IZ.SPS | Sacral Parasympathetic Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) | |
| LAC.SC.LH.LSN | Lateral Spinal Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) | |
| LMC | LMC.HL.RP.MG | Raphe Magnus Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
| LPC | LPC.SC.VH.ONF | Onuf's Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
| TEA | TARGET.TEA.ENDOCRINE | Endocrine Glands | endocrine-neurohypophysis-oxytocin | Amygdalar disruption of prefrontal cortex (HT.PV -> PUT) |
Thirdparty Circuits
(generated)




- Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance - see Reference

References
(generated)
- http://neuropolitics.org/defaultmay10.asp
- http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html
- http://www.dana.org/Publications/ReportDetails.aspx?id=44217
- http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders
- http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf