MindTractsDT
From aHuman Wiki
Biological Mind Tracts
Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> MindTracts -> MindTractsDT

This page is intended to describe set of descending tracts
Contents
[hide]Tract Details
(generated)
TRACT SET: Descending Tracts
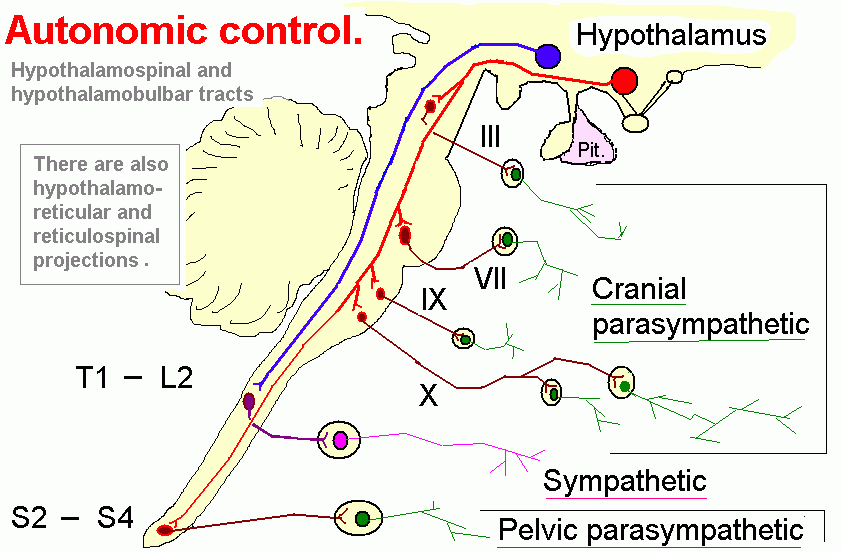
ATS - autonomic tracts system
- external:
- synonyms: descending autonomic fibers
- function:directs activity of glands, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscle
- generic path: {cortex, HT, AM, RF} -> {sympathetic and parasympathetic}
HTST - hypothalamospinal tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamospinal_tract
- function:control autonomic components
- comments: descend in dorsolateral funiculus; oculosympathetic pathway; next to superior cervical ganglion to common carotid - internal carotid - long ciliary nerves to pupillary dilator
- notes to function:
- descend in dorsolateral funiculus
- oculosympathetic pathway
- next to superior cervical ganglion to common carotid - internal carotid - long ciliary nerves to pupillary dilator
- generic path: {paraventrical nucleus of hypothalamus} -> {IML, sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons; ciliospinal center of IML (T1,T2)}
Tract path details:
- path HTST.CSC: stress responses (from paraventricular and lateral hypohtalamus to IML and SPS) - Paraventricular Nucleus,LAC.FD.HT.PV -> Ciliospinal Center,LAC.SC.IZ.CSC
- path HTST.IML: blood pressure regulation (from paraventricular and lateral hypohtalamus to IML and SPS) - Paraventricular Nucleus,LAC.FD.HT.PV -> Intermediolateral Nucleus,LAC.SC.IZ.IML
SSS - solitariospinal system
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Respiratory_system
- function:autonomic control of breathing
- comments: respiratory, vomiting and micturition functions
- notes to function:
- respiratory, vomiting and micturition functions
- generic path: {ventrolateral solitary nucleus, retroambiguus nucleus} -> {diaphragm}
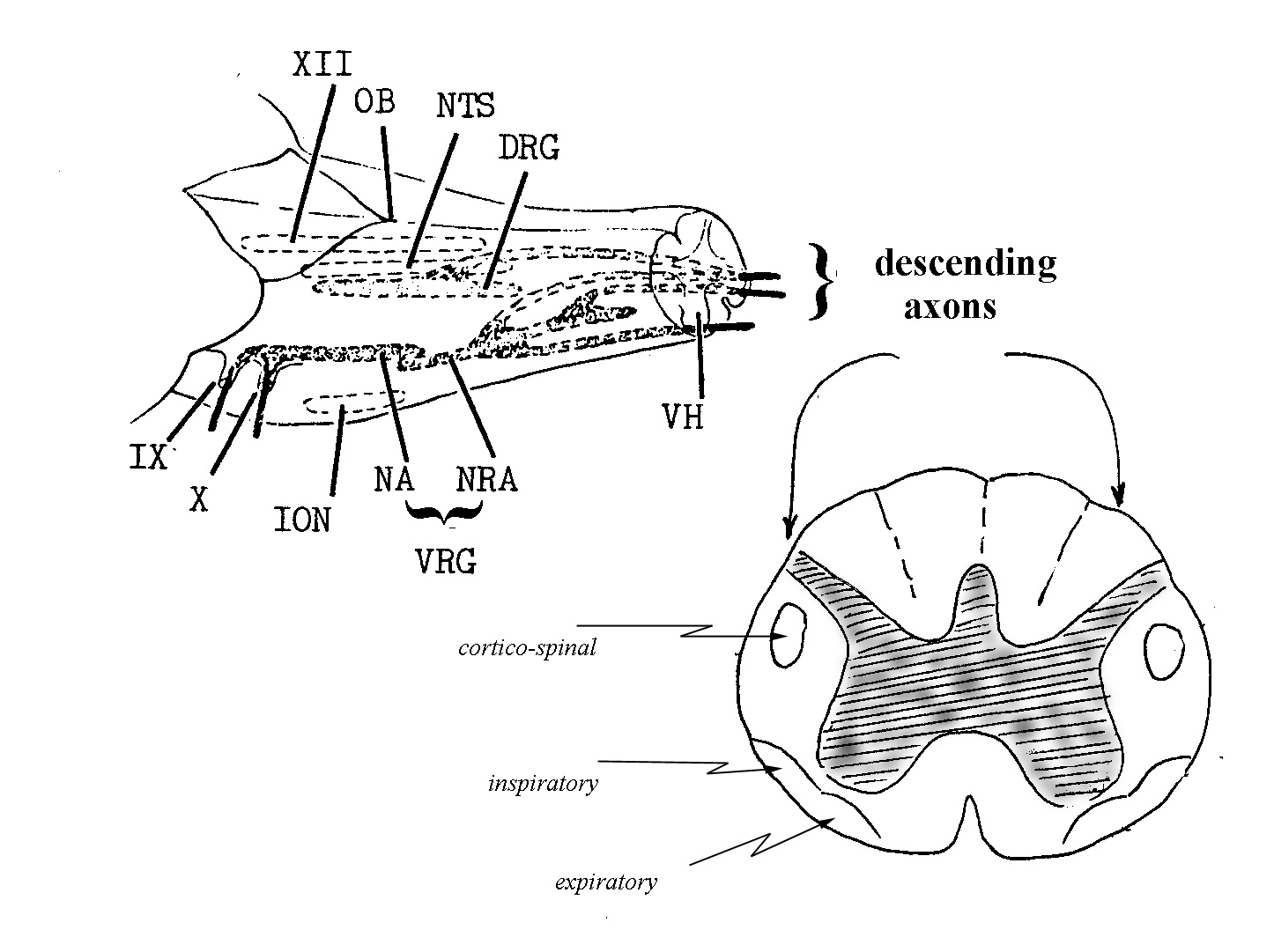
SSET - solitariospinal expiratory tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ventral_respiratory_group
- function:facilitate expiratory motor neurons to intercostal muscles
- comments: nucleus ambiguus - cranial division innervates muscles of the ipsilateral accessory muscles of respiration, principally via the vagus; nucleus retroambiguus - caudal division provides inspiratory and expiratory drive to the motor neurones of the intercostal muscles
- notes to function:
- nucleus ambiguus - cranial division innervates muscles of the ipsilateral accessory muscles of respiration, principally via the vagus
- nucleus retroambiguus - caudal division provides inspiratory and expiratory drive to the motor neurones of the intercostal muscles
- generic path: {parabrachial nucleus to nucleus ambiguus, nucleus retroambiguus} -> {internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles}

Tract path details:
- path SSET.PATH: facilitary expiratory muscles (descending in ventral funiculus) - Ambiguus Nucleus,LPC.HL.AMB -> Ventromedial Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.VM
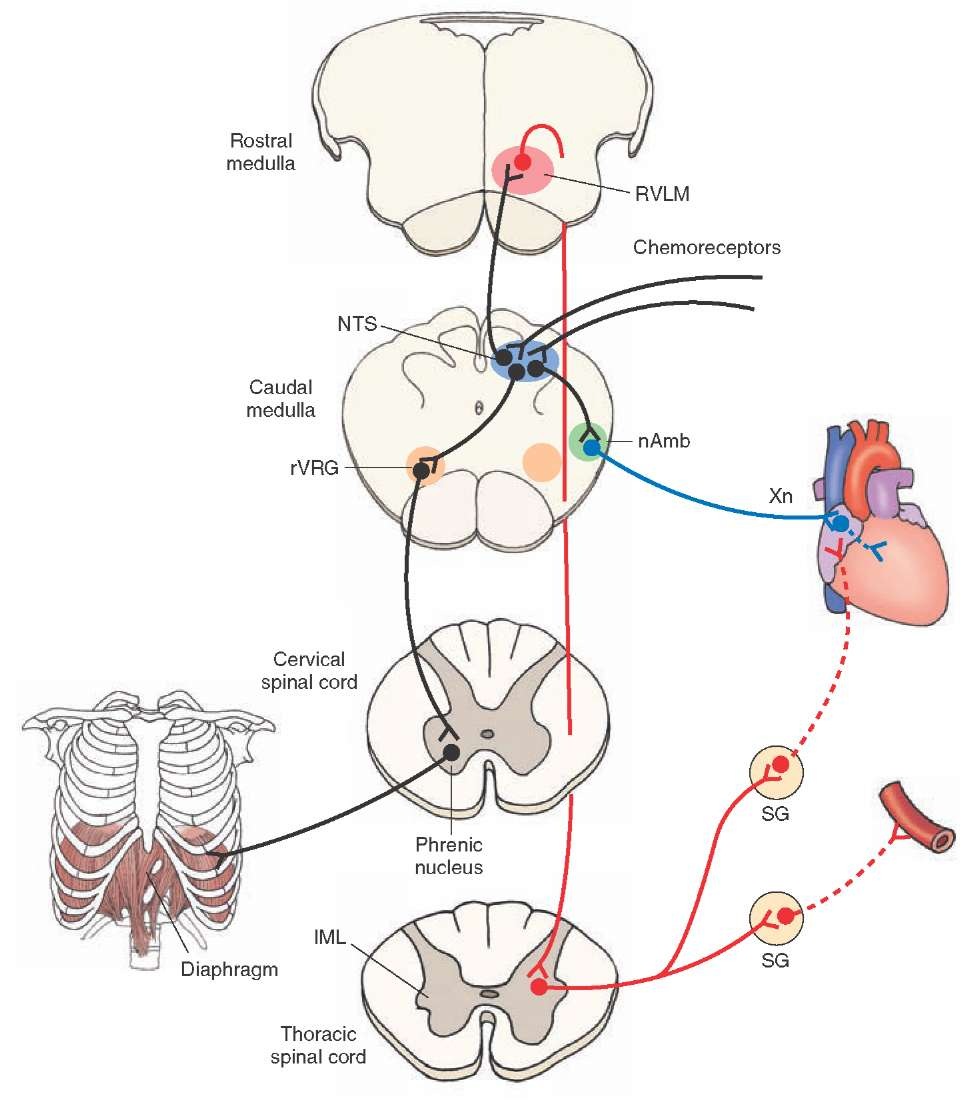
SSIT - solitariospinal inpiratory tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dorsal_respiratory_group
- function:facilitate inspiratory motor neurons in phrenic nucleus
- comments: neck muscles, external intercostal muscles - conscious forced inspiration; pneumotaxic center = medial parabrachial nucleus + kolliker-fuse nucleus, breathing frequency
- notes to function:
- neck muscles, external intercostal muscles - conscious forced inspiration
- pneumotaxic center = medial parabrachial nucleus + kolliker-fuse nucleus, breathing frequency
- generic path: {kolliker-fuse nucleus, receptors to solitary nucleus} -> {phrenic nucleus, inspiratory; diaphragm}
Tract path details:
- path SSIT.PATH: driving inspiratory muscles (descending in ventral part of lateral funiculus) - Kolliker-Fuse Nucleus,LRC.HT.KFN -> Phrenic Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.PHR
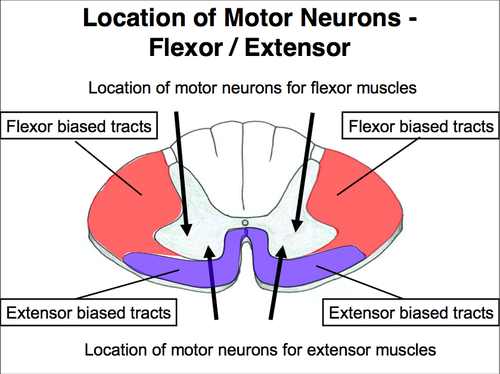
ESS - extensor somatic system
- external:
- function:control extensor muscles
ACST - anterior corticospinal tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_corticospinal_tract
- synonyms: ventral corticospinal tract
- function:extensor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious
- comments: premotor BA 6, parietal BA 1,2,3
- notes to function:
- premotor BA 6, parietal BA 1,2,3
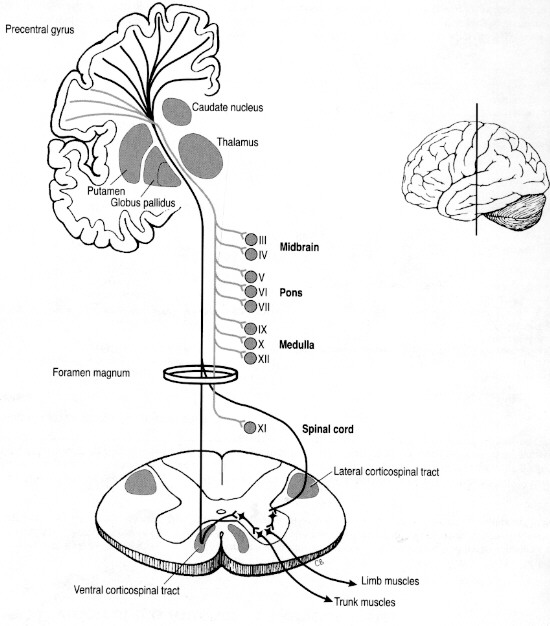
Tract path details:
- path ACST.VL: conscious control of distal extensors (premotor cortex to spinal cord VL) - Dorsal Caudal Premotor Cortex,NMA.NC.PMC.F2 -> Ventrolateral Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.VL
- path ACST.VM: conscious control of axial extensors (premotor cortex to spinal cord VM) - Supplementary Motor Area,NMA.NC.SMC.F3 -> Ventromedial Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.VM
MLFS - medial longitudinal fasciculus system
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medial_longitudinal_fasciculus
- function:connects the cranial nerve nuclei III (oculomotor nerve), IV (trochlear nerve) and VI (abducens nerve) together, and integrates movements directed by the gaze centers (frontal eye field) and information about head movement (from cranial nerve VIII, vestibulocochlear nerve)
- comments: connects together III, IV, and VI; integral component of saccadic eye movements as well as vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic reflexes; tectospinal and vestibulospinal
- notes to function:
- connects together III, IV, and VI
- integral component of saccadic eye movements as well as vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic reflexes
- tectospinal and vestibulospinal
- generic path: {vestibular nucleus} -> {}
TCST - tectospinal tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tectospinal_tract
- function:mediate reflex postural movements of head in response to visual and auditory stimuli
- comments: extrapyramidal; in response to bright and sudden movements and loud noises
- notes to function:
- extrapyramidal
- in response to bright and sudden movements and loud noises

Tract path details:
- path TCST.DEEP: coordinates head and eye movements; mediate reflex postural movements of head in response to visual stimuli (from deep layers of the superior colliculus; projects to contralateral and ipsilateral portion of first cervical neuromeres of spinal cord, oculomotor and trochlear nuclei and abducens nucleus) - Deep Superior Colliculus,LRC.MM.SC.DEEP -> Spinal Accessory Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.SAN
- path TCST.INT: coordinates head and eye movements; mediate reflex postural movements of head in response to auditory and somatosensory stimuli (from intermediate layers of the superior colliculus; projects to contralateral and ipsilateral portion of first cervical neuromeres of spinal cord, oculomotor and trochlear nuclei and abducens nucleus) - Deep Superior Colliculus,LRC.MM.SC.DEEP -> Spinal Accessory Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.SAN
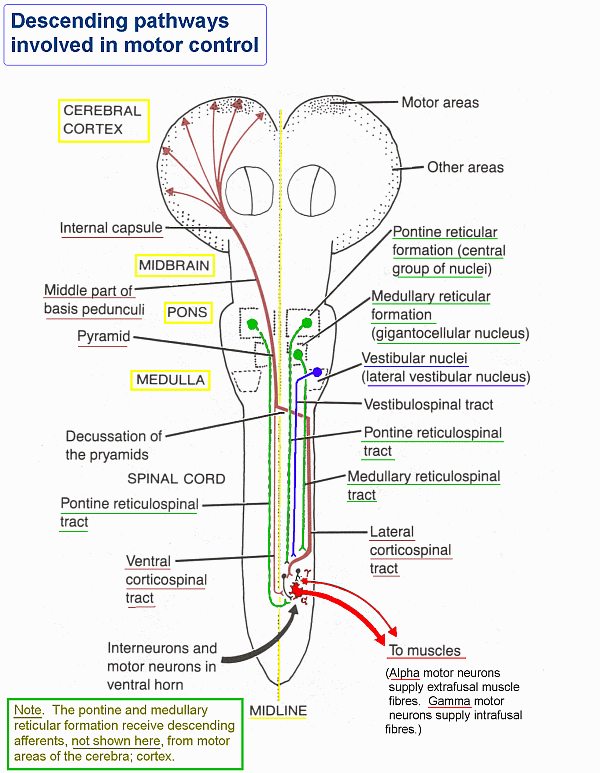
VST - vestibulospinal tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vestibulospinal_tract
- function:alter muscle tone, extend, and change position of limbs and head with goal of supporting posture and maintaining balance of body and head; maintain balance and to stabilize the visual image on the retina during head movements
- comments: extrapyramidal; proximal muscles, postural control; activates extensors, inhibits flexors; vestibular nuclei receive their primary input from the vestibular portion of C.N. VIII - vestibular-auditory
- notes to function:
- extrapyramidal
- proximal muscles, postural control
- activates extensors, inhibits flexors
- vestibular nuclei receive their primary input from the vestibular portion of C.N. VIII - vestibular-auditory

LVST - lateral vestibulospinal tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lateral_vestibulospinal_tract
- function:maintain an upright and balanced posture by stimulating extensor motor neurons in legs
- comments: also innervates muscles of the trunk, thus additionally aiding in body posture; lateral vestibular nuclei receive input from cerebellum
- notes to function:
- also innervates muscles of the trunk, thus additionally aiding in body posture
- lateral vestibular nuclei receive input from cerebellum
- generic path: {lateral vestibular nucleus; additional input from superior and inferior vestibular nuclei} -> {extensor muscles of legs}

Tract path details:
- path LVST.PATH: maintain an upright and balanced posture by stimulating extensor motor neurons in legs (originating in lateral, superior, and inferior vestibular nuclei (primarily the lateral); projects ipsilaterally down to lumbar region of spinal cord) - Lateral Vestibular Nucleus,LPC.HT.LVBN -> Ventrolateral Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.VL
MVST - medial vestibulospinal tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medial_vestibulospinal_tract
- function:controls position of the head, neck, and eyes in response to changes in posture
- comments: controlling lower motor neurons associated with the spinal accessory nerve - CN XI; additionally, projects superiorly to the paramedian pontine reticular formation, indirectly innervating the nuclei of CN VI and III
- notes to function:
- controlling lower motor neurons associated with the spinal accessory nerve - CN XI
- additionally, projects superiorly to the paramedian pontine reticular formation, indirectly innervating the nuclei of CN VI and III
- generic path: {medial vestibular nucleus} -> {spinal accessory nucleus, paramedian pontine reticular formation; found only in cervical spine and above}

Tract path details:
- path MVST.PATH: it controls head and whole body orientation (from medial vestibular nucleus; projects bilaterally down spinal cord and triggers ventral horn of cervical spinal circuits) - Medial Vestibular Nucleus,LPC.HT.MVBN -> Spinal Accessory Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.SAN
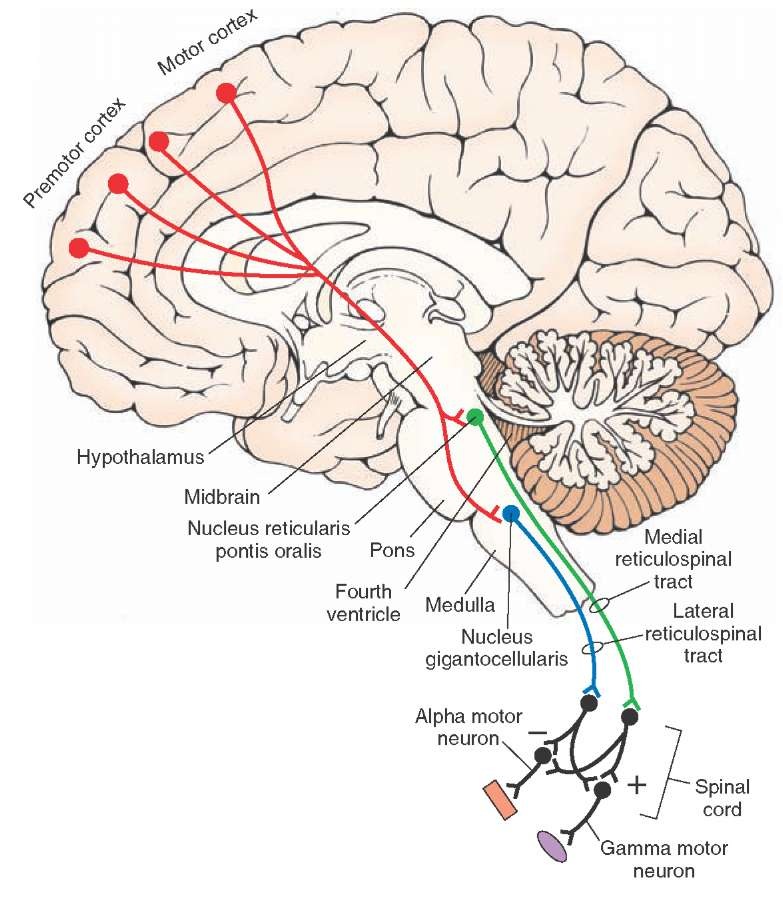
RTSS - reticulospinal system
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reticulospinal_tract
- function:locomotion and postural control
- comments: extrapyramidal; proximal muscles, postural control; integrates information from the motor systems to coordinate automatic movements of locomotion and posture; facilitates and inhibits voluntary movement; influences muscle tone; mediates autonomic functions; modulates pain impulses; influences blood flow to lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus
- notes to function:
- extrapyramidal
- proximal muscles, postural control
- integrates information from the motor systems to coordinate automatic movements of locomotion and posture
- facilitates and inhibits voluntary movement
- influences muscle tone
- mediates autonomic functions
- modulates pain impulses
- influences blood flow to lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus
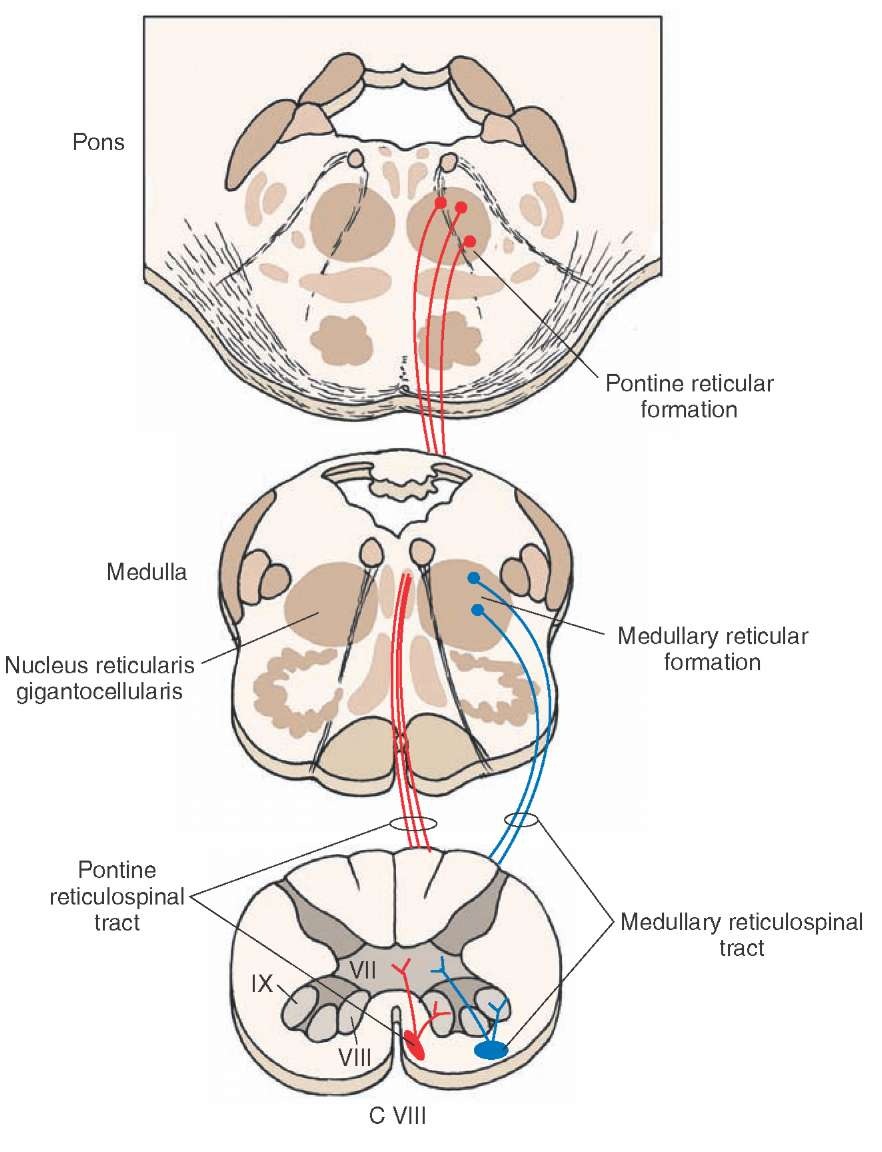
MRST - medullary reticulospinal tract
- external:
- synonyms: lateral reticulospinal tract
- function:inhibiting excitatory axial extensor muscles of movement
- generic path: {Gigantocellular Reticular Nucleus} -> {extensor muscles, all levels of spinal cord}
Tract path details:
- path RTSS.MGC: coordinate with phasic movements to and from paradoxical sleep; inhibit with enkephalin (from nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis (vasodepressor center) to lamina VII) - Gigantocellular Reticular Nucleus,LRC.HL.PRF.GCR -> Intermediolateral Nucleus,LAC.SC.IZ.IML
PRST - pontine reticulospinal tract
- external:
- synonyms: medial reticulospinal tract
- function:exciting anti-gravity, extensor muscles; mediate postural adjustments in response to startling stimuli
- generic path: {Pontine Reticular Formation } -> {extensor muscles, all levels of spinal cord}
Tract path details:
- path RTSS.PNC: mediate head movement, suppresses muscle tone during REM sleep (from caudal pontine reticular nucleus to lamina VII and lamina VIII of spinal cord) - Caudal Pontine Reticular Nucleus,LRC.HT.PRF.CRF -> Ventromedial Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.VM
- path RTSS.PNO: coordinate with phasic movements to and from paradoxical sleep (from oral pontine reticular nucleus to lamina VII and lamina VIII of spinal cord) - Oral Pontine Reticular Nucleus,LRC.HT.PRF.RPO -> Ventromedial Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.VM
FSS - flexor somatic system
- external:
- function:control flexor muscles
CBT - corticobulbar tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticobulbar_tract
- function:carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves
- comments: V, VII, XI, and XII; indirectly - via IX and X in nucleus ambiguus
- notes to function:
- V, VII, XI, and XII
- indirectly - via IX and X in nucleus ambiguus
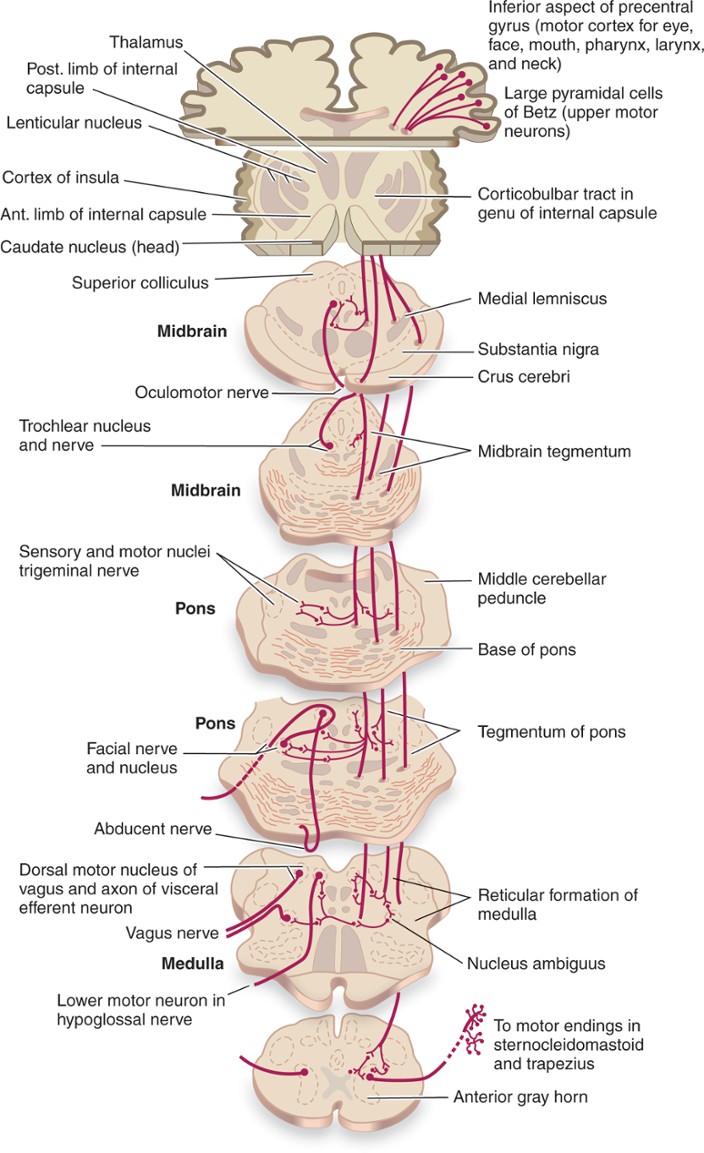
Tract path details:
- path CBT.FACE: conscious face expression (cortex to face muscles) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Facial Motor Nucleus,LPC.HT.FCM
- path CBT.MOUTH: conscious jaw move (cortex to jaw muscles) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Trigeminal Motor Nucleus,LPC.HT.TRM
- path CBT.NECK: conscious neck move (cortex to neck muscles) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Spinal Accessory Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.SAN
- path CBT.THROAT: conscious pharynx/larynx move (cortex to throat muscles) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Ambiguus Nucleus,LPC.HL.AMB
- path CBT.TONGUE: conscious tongue move (cortex to tongue muscles) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Hypoglossal Motor Nucleus,LPC.HL.HYG
LSTT - lateral corticospinal tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lateral_corticospinal_tract
- function:flexor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious; volitional skilled motor activity
- comments: 90 percents of corticospinal fibers; 80 percents - contrallateral; 10 percents - unilateral; cervical-medial, thoracic, lumbar-lateral, distal muscles, decussating to contralateral and ipsilateral
- notes to function:
- 90 percents of corticospinal fibers
- 80 percents - contrallateral
- 10 percents - unilateral
- cervical-medial, thoracic, lumbar-lateral, distal muscles, decussating to contralateral and ipsilateral
- generic path: {cortex BA 1-4,6} -> {muscle groups that require concentration and conscious thought to control; upper limb digits}

Tract path details:
- path LCST.PL: conscious control of proximal flexors (cortex to spinal cord PL) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Posterolateral Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.PL
- path LCST.PM: conscious control of axial flexors (cortex to spinal cord PM) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Posteromedial Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.PM
- path LCST.RPL: conscious control of distal flexors (cortex to spinal cord RPL) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Retroposterolateral Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.RPL
RBST - rubrospinal tract
- external: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rubrospinal_tract
- function:mediation of voluntary movement, upper limbs; control of flexor tone
- comments: extrapyramidal; activates flexors, inhibits extensors; pattern locomotion, inhibit reflex activity in spinal cord; terminate into dorsal horn and in the intermediate region of the ventral horn; fibers terminated in contralateral laminae 5, 6, and the dorsal part of lamina 7 at all spinal cord levels
- notes to function:
- extrapyramidal
- activates flexors, inhibits extensors
- pattern locomotion, inhibit reflex activity in spinal cord
- terminate into dorsal horn and in the intermediate region of the ventral horn
- fibers terminated in contralateral laminae 5, 6, and the dorsal part of lamina 7 at all spinal cord levels

Tract path details:
- path RBST.CR: automatic control of flexors (cerebellum to red nucleus) - Cerebellum,LLC.HT.CR (Cerebellar Flocconodular Lobe (LRC.HT.CR.FN), Cerebellar Lateral Lobe (LLC.HT.CR.CC), Cerebellar Paravermis (LLC.HT.CR.PV), Cerebellar Vermis (LRC.HT.CR.VM)) -> Red Nucleus,LLC.MM.RD
- path RBST.MC: conscious modulation of automatic flexors activity (cortex to red nucleus) - Motor Cortex,NMA.NC.MC -> Red Nucleus,LLC.MM.RD
- path RBST.PL: automatic control of proximal flexors (red nucleus to spinal cord PL) - Red Nucleus,LLC.MM.RD -> Posterolateral Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.PL
- path RBST.PM: automatic control of axial flexors (red nucleus to spinal cord PM) - Red Nucleus,LLC.MM.RD -> Posteromedial Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.PM
- path RBST.RPL: automatic control of distal flexors (red nucleus to spinal cord RPL) - Red Nucleus,LLC.MM.RD -> Retroposterolateral Nucleus,LPC.SC.VH.RPL