Difference between revisions of "BrainCenterFAM FT AM"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
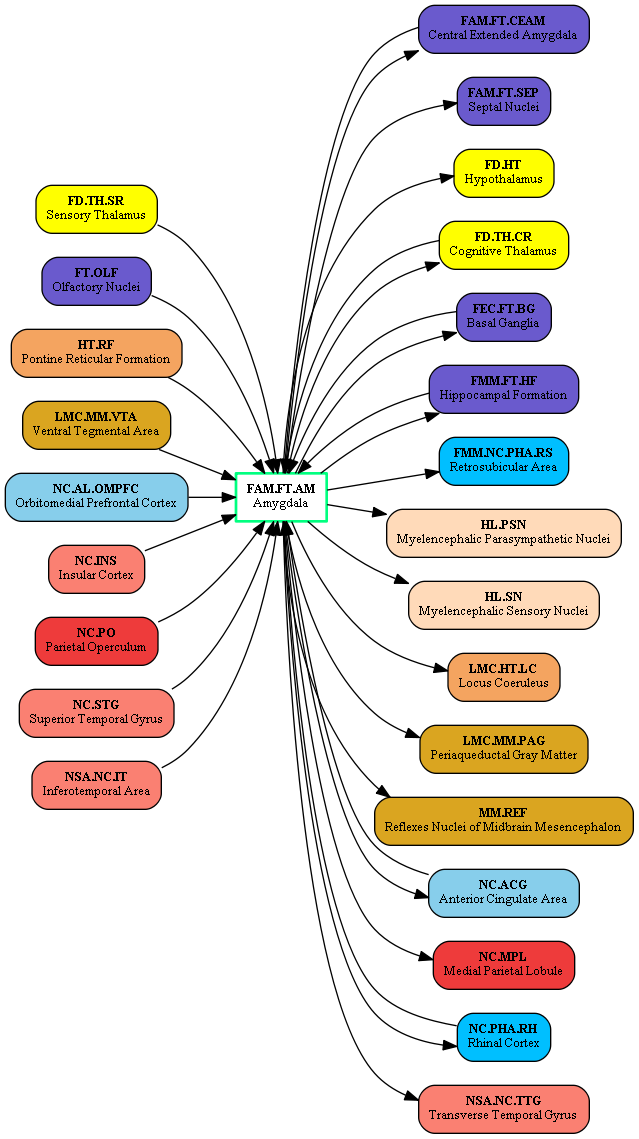
| [[BrainCenterNC_AL_OMPFC|Orbitomedial Prefrontal Cortex]] (NC.AL.OMPFC) || [[BrainRegionNDM_NC_AL_FPC|NDM.NC.AL.FPC]] -> [[BrainRegionFAM_FT_AM_BM|FAM.FT.AM.BM]]||[http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/fig_tab/nrendo.2010.93_F1.html Bowels control brain: gut hormones and obesity (OFC -> AMY, abstract)] | | [[BrainCenterNC_AL_OMPFC|Orbitomedial Prefrontal Cortex]] (NC.AL.OMPFC) || [[BrainRegionNDM_NC_AL_FPC|NDM.NC.AL.FPC]] -> [[BrainRegionFAM_FT_AM_BM|FAM.FT.AM.BM]]||[http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/fig_tab/nrendo.2010.93_F1.html Bowels control brain: gut hormones and obesity (OFC -> AMY, abstract)] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[BrainCenterNC_INS|Insular Cortex]] (NC.INS) || [[BrainRegionNCP_NC_INS_PIC|NCP.NC.INS.PIC]] -> [[BrainRegionFAM_FT_AM_BM|FAM.FT.AM.BM]]||( | + | | [[BrainCenterNC_INS|Insular Cortex]] (NC.INS) || [[BrainRegionNCP_NC_INS_PIC|NCP.NC.INS.PIC]] -> [[BrainRegionFAM_FT_AM_BM|FAM.FT.AM.BM]]||[http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v14/n7/fig_tab/nrn3516_F2.html Afferent pain pathways (Insula -> AMY, abstract)] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[BrainCenterNC_PHA_RH|Rhinal Cortex]] (NC.PHA.RH) || [[BrainRegionFMM_NC_PH_LEC|FMM.NC.PH.LEC]] -> [[BrainRegionFAM_FT_AM_AB|FAM.FT.AM.AB]]||[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030100820900183X Simplified model of hippocampal formation anatomy (EC -> Amyg, abstract)] | | [[BrainCenterNC_PHA_RH|Rhinal Cortex]] (NC.PHA.RH) || [[BrainRegionFMM_NC_PH_LEC|FMM.NC.PH.LEC]] -> [[BrainRegionFAM_FT_AM_AB|FAM.FT.AM.AB]]||[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030100820900183X Simplified model of hippocampal formation anatomy (EC -> Amyg, abstract)] | ||
Revision as of 08:14, 21 September 2015
Amygdala
@@Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> BrainCenterFAM_FT_AM
This page covers biological details of component group Amygdala. Component group is part of aHuman target integrated biological model.
- Top-down path to center: Forebrain Telencephalon -> Extended Amygdala (FAM.FT.EXTAM) -> Amygdala (FAM.FT.AM) (see Mind Maps)
- Function: Experiencing and recognizing emotions
(generated)
Components
(generated)
Component items:
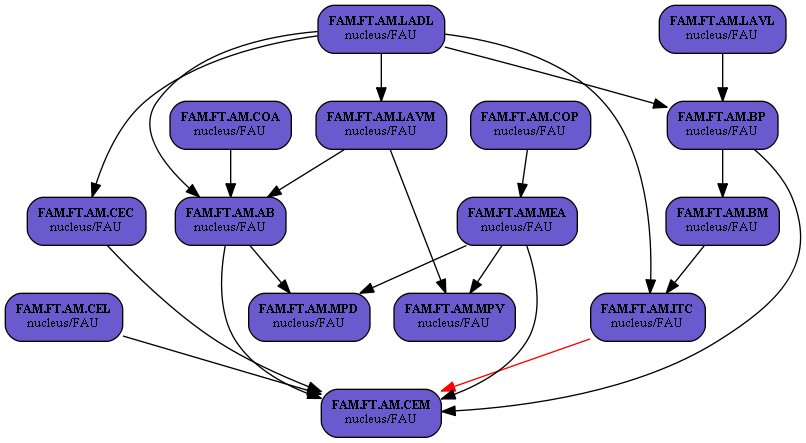
- Basolateral Nuclear Complex (FAM.FT.AM.BL): stimulating emotional response
- Lateral Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.LA): plasticity, conditional (neutral stimulus) to specific (taste, smell, visceral) unconditional (positive or negative stimulus) association
- Dorsolateral Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.LADL): conditional stimulus input - high-aggregated visual, auditory and somatic, patterns of perception
- Ventrolateral Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.LAVL): unconditional stimulus input - visual, auditory and somatic, convergence from thalamus
- Ventromedial Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.LAVM): conditional and unconditional convergence to affect polymodal memory formation
- Basal Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.B): enhance explicit memories in hippocampus about emotional situations
- Parvicellular Basal Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.BP): enhance explicit memories in hippocampus about emotional situations
- Magnocellular Basal Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.BM): enhance emotional memories memories in medial prefrontal cortex
- Accessory Basal Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.AB): enhance assotiative memory formation
- Lateral Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.LA): plasticity, conditional (neutral stimulus) to specific (taste, smell, visceral) unconditional (positive or negative stimulus) association
- Corticomedial Nuclear Complex (FAM.FT.AM.CTM)
- Cortical Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.CO): olfactory processing
- Anterior Cortical Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.COA): olfactory processing - conditional contextual signaling
- Posterior Cortical Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.COP): olfactory processing - unconditional signaling
- Centromedial Nuclei (FAM.FT.AM.CM): attention and arousal
- Central Amygdala (FAM.FT.AM.CEA): mediate behavioral responses, link to general aspects of reinforcement; responses to fear stimuli; directing attention and behaviors when salience of competing stimuli is in flux
- Central Amygdaloid Nucleus, capsular subdivision (FAM.FT.AM.CEC): mediate behavioral responses, link to striatal effect
- Central Amygdaloid Nucleus, lateral subdivision (FAM.FT.AM.CEL): mediate behavioral responses, link to gustatory and visceral aspects of reinforcement
- Medial Central Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.CEM): mediate behavioral responses, output projections
- Medial Amygdala (FAM.FT.AM.M): sense of smell and pheromone-processing
- Medial Anterior Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.MEA): olfactory processing
- Medial Posterior Dorsal Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.MPD): reproductive behavior
- Medial Posterior Ventral Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.MPV): defensive behavior
- Central Amygdala (FAM.FT.AM.CEA): mediate behavioral responses, link to general aspects of reinforcement; responses to fear stimuli; directing attention and behaviors when salience of competing stimuli is in flux
- Cortical Amygdaloid Nucleus (FAM.FT.AM.CO): olfactory processing
- Intercalated Amygdaloid Nuclei (FAM.FT.AM.ITC): inhibit excessive emotional behavior
Connectivity
(generated)
Internal Regions Connections:
External Connections:
External Inbound Center Connections:
External Outbound Center Connections: